PARALLEL
OPERATION OF DC GENERATORS
From the view of connections there are two types named series
and parallel. In series connection one end is connected to supply and other end
is connected to other device. In parallel connection every device is connected to both
positive and negative terminals
* In series connections voltage is differ and current is same,
due to this reason if one generator fails to working the other devices stop
working.
* In parallel connection current is differ and voltage is same,
due to this reason if one generator fails to working the other devices run
without any disturbance.
Advantages of parallel connection over series connection:
1.Continuity and Reliability of service
2. Maintenance and repair
3. efficiency
4. Increase in plant capacity
The below figure shows the two generators connected in
parallel:
When two generators are in running condition the current
supplied by the generator is necessary that its induced EMF should be more than
the bus bar voltage.
At starting position the prime mover provides the Mechanical energy and
the speed is adjusted by the field rheostat. One another advantage in
connecting parallel is the load sharing by the two generators.
* If any one of generators fails the other will work without
any disturbance to remove the failed generator we have to open the switch S1 and S3 while the
voltmeter of another generator shows zero readings or equal potential between
induced EMF and bus bars.
* If the generator is connected in reverse polarity to the
bars it results in short circuit which causes damages to the machines and
occurs a change to shut down the station.
If E =
Induced EMF
V =
Bus bar voltage
Then current supplied by I is given as
Ia = E – V/Ra
Proceeding:
The below steps should adopted while operating the generators
in parallel:
1. Start the prime mover of generator and adjust with rated
speed.
2.Close the disconnected switch of the Incoming generator.
3. The generator excitation is adjusted to few volts more
than bus bar voltage.
4. Close the generator breaker.
5. The voltage is increased by adjusting the field rheostat.
Differences between the generator operated in parallel:
|
|
Shunt Generator
|
Series Generator
|
Compound Generator
|
|
1.
|
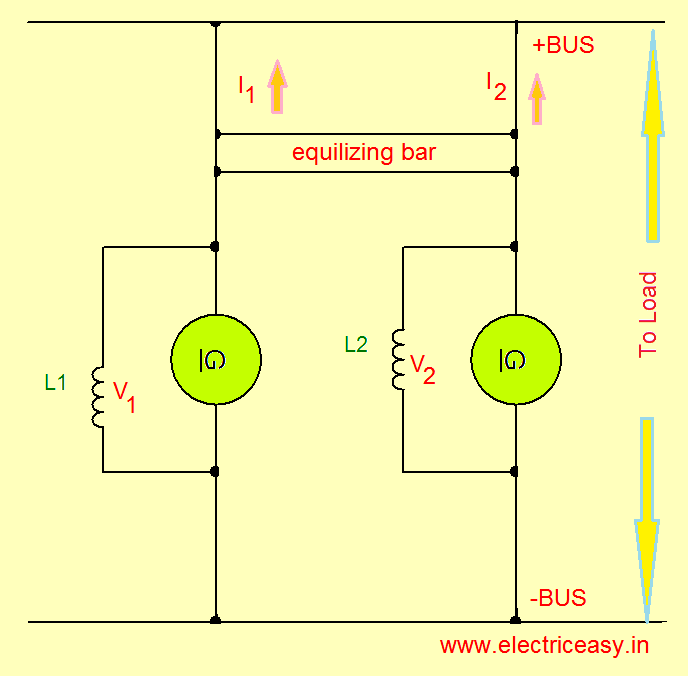
No equalizing bar is required
|
Equalizing bar is needed to share the load
|
Equalizing
bar is needed to share the load (But for satisfactory operation of compound
type no need of equalizers)
|
|
2.
|
Two parallel shunt generators having equal no load
voltage share the load in such a ratio that the load current of each machine
produces the same drop in each generator
|
If no load
voltage E1 and E2 of
the two generators are initially same, generators supply equal currents and
have equal resistance for its field winding.
|
The regulation of each generator is same.
|
|
3.
|
The work is shared by the two generators without
equalizing bar.
|
The work is
shared with the help of equalizing bar if it is not shared the entire load
will fall on single generator and there is a chance to destroy the machine
|
The work is shared in over compound and level
compound by using equalizing bar if not the generator 1 will take load and
destroys the Machine.
|
* The below circuit diagrams shows the types of generators
connected in parallel
* The Compound generator operated in parallel
* The series generator operated in parallel
* The shunt generator operated in parallel



No comments:
Post a Comment